Agile HR is a modern approach to human resources that emphasizes flexibility, adaptability, and continuous improvement. In today’s fast-paced corporate environment, traditional HR practices struggle to keep up. Agile HR applies principles from agile methodologies, making HR more responsive to change and better aligned with business needs.
Some HRIS systems are incorporating modules within their existing software that promote agile HR strategies, but Agile HR is not an HRIS system in and of itself. This article will explore essential strategies and principles of Agile HR, and how they transform the HR function to meet the demands of modern organizations.
Key Takeaways
- Agile HR integrates Agile principles into human resources, emphasizing flexibility, adaptability, and continuous improvement to better meet the dynamic needs of modern organizations.
- Implementing Agile HR involves setting clear goals, forming cross-functional teams, and using Agile frameworks like Scrum and Kanban to enhance collaboration, responsiveness, and continuous improvement.
- Agile HR promotes continuous performance management through regular feedback loops and employee empowerment, fostering an engaged workforce and a culture of innovation and psychological safety.
Understanding Agile for HR

Agile HR applies Agile methodologies in the human resources field, highlighting flexibility, adaptability, and continuous improvement in the management of people and processes. Agile, which originated from software development in the late 1990s, was a response to the need for delivering products in a continuously changing market environment. It was developed to address the challenges of traditional software development methods that, due to rapidly changing requirements, were often outdated by the time the applications were completed.
Agile HR integrates many of the same principles into HR practices, reshaping the human resources function to become more responsive and swiftly adapt to evolving situations. This agile approach emphasizes speed, flexibility, and collaboration, creating a responsive and adaptive function for the HR professional that can better meet the needs of modern organizations.
The Importance of an Agile HR Strategy in Today’s Business Environment

Traditional HR practices, burdened by compliance-driven, bureaucratic, and siloed structures, find it challenging to keep up with the swift changes in the contemporary business landscape. Static frameworks and best practices fail to address the needs of a multi-generational and diverse workforce.
Agile HR, on the other hand, emphasizes iterative development, collaboration, and customer feedback, making HR systems and processes more dynamic and responsive to change. This agile human resources approach allows organizations to quickly adapt to organizational challenges, ultimately leading to increased employee satisfaction and enhanced organizational performance.
Moreover, Agile HR plays a fundamental role in the adoption of an agile culture within organizations. HR professionals are uniquely positioned to design new organizational structures that enable business agility, maximize communication and collaboration, and facilitate the flow of value.
Agile HR aids organizations in navigating the intricacies of the modern business environment and maintaining competitiveness by revolutionizing how they hire, develop, and manage their workforce. The benefits of adopting Agile human resources are clear: enhanced agility, prompt responses to customer needs, and a more engaged and satisfied workforce.
Core Principles of Agile for Human Resources

Three core principles form the essence of Agile HR, embodying the agile principles: prioritizing collaboration over hierarchy, being responsive to change, and encouraging continuous improvement. These principles guide the agile approach to HR, shifting the focus from strict controls and standards to facilitating and improving organizational agility.
An agile HR approach empowers organizations to be more innovative and responsive to dynamic business needs by nurturing a collaborative environment, highlighting adaptability, and endorsing continuous development through the implementation of an agile HR model. By fostering an agile HR team, organizations can achieve these goals more effectively.
Collaboration Over Hierarchy
Agile HR fosters a dynamic environment built on collaboration, innovation, and open communication. It prioritizes a network of collaborative teams over traditional hierarchical structures.
By bridging gaps between traditionally siloed teams and fostering cross-functional collaboration, Agile HR enhances teamwork and ensures that all employees, regardless of their job titles, can contribute their unique skills to projects. Picture key team members from IT, Marketing, and HR discussing the latest employer branding strategy and how it will be portrayed on the website. Without collaboration and Agile HR, accomplishing what should be a three-week task may take months as it passes through various approvals and departmental red tape.
This approach not only promotes a more inclusive and innovative organizational culture but also ensures that the HR function is more responsive and adaptable to changing business needs in a timely manner.
Responsiveness to Change
Agile HR prioritizes speed and adaptability. Its solutions are developed in an iterative and incremental manner, enabling HR teams to effectively respond to fluctuating career demands and business requirements. This agile approach shifts the focus from strict controls and standards to facilitating and improving organizational agility, enabling HR teams to quickly adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
The result is that some companies will still be writing job descriptions while others are interviewing already. By emphasizing responsiveness to change, Agile HR ensures that organizations can remain competitive and innovative in the rapidly evolving world of business.
Continuous Improvement
Agile HR places significant emphasis on promoting continuous development and innovation. Work is carried out in sprints, which are 2- to 4-week periods where the team delivers an initial version of the solution, gathers feedback, and repeats the process. This iterative approach ensures that HR practices are constantly evolving and improving, fostering a culture of adaptability and relentless improvement.
By regularly assessing and refining HR processes, an agile approach helps organizations stay ahead in a competitive landscape.
Implementing Agile Methodology in HR Practices
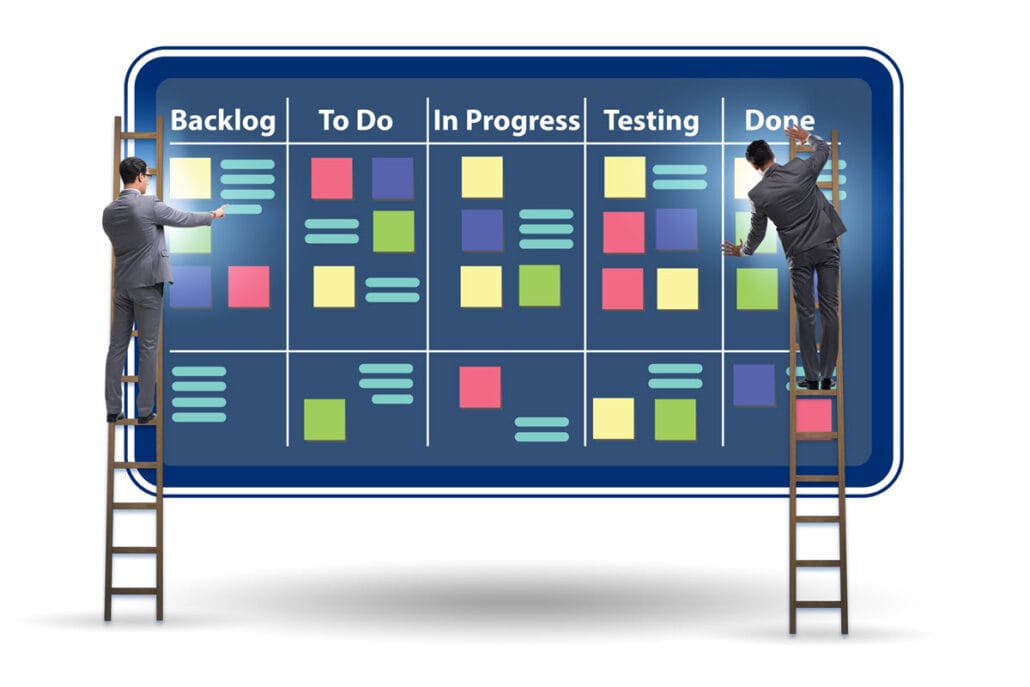
The implementation of Agile methodology in HR practices encompasses key steps such as defining explicit goals, forming cross-functional teams, and applying agile frameworks.
The first step is to develop clear goals and objectives for the Agile HR initiative, ensuring they align with overall business objectives. This requires effective allocation of resources, including time, budget, and skilled personnel.
Next, assembling cross-functional teams is crucial. These teams should include members with diverse skills and perspectives, fostering innovation and collaboration.
Utilizing agile frameworks like Scrum and Kanban help make project management more effective, and promotes iterative development.
Define Clear Goals and Objectives
In Agile HR, establishing explicit and attainable goals is vital. These goals should be developed collaboratively with input from the entire team to ensure they are relevant and attainable.
Using the SMART goals framework (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) can increase the chances of achieving defined Agile HR goals. Key elements include:
- Clear goals
- Talent needs assessment
- Open communication
- Flexible job roles
Assemble Cross-Functional Agile HR Teams
The Agile methodology regards cross-functional teams as a fundamental element. These teams bring together members with diverse skills and perspectives, fostering innovation and collaboration. Agile HR teams are typically small, nimble, and work in sprints to tackle specific goals.
By including a variety of HR professionals including HR generalists, recruiters, and IT personnel, the HR team can develop solutions collaboratively and effectively. Selecting team members for Agile HR initiatives should be based on their skills, experience, and willingness to embrace change and the agile mindset.
Utilize Agile Frameworks
Managing HR projects effectively is facilitated by Agile frameworks such as Scrum and Kanban.
Scrum is built on a foundation of trust, with building blocks of transparency, inspection, and adaptation. In HR, this involves breaking down projects into smaller goals. Goals are then set for “sprints” (a short, focused burst of work typically lasting for 2 weeks). At the end of sprints, the HR team takes what they’ve learned from the sprint and adapt accordingly to refine and enhance the next sprint.
Kanban, on the other hand, utilizes a visual board to manage workflow, with tasks represented by cards moving across different stages. This allows HR teams to identify bottlenecks and gives a quick, visual insight into the status of projects and processes.
These frameworks, while initially developed for software development, have proven to be highly effective in an Agile HR model, promoting iterative development and continuous improvement across human resources in an organization.
Agile Performance Management

Agile performance management substitutes traditional annual reviews with continuous feedback loops, fostering employee engagement and empowerment. This approach involves frequent check-ins and real-time feedback, allowing for immediate course corrections and performance improvement.
Agile feedback processes facilitate:
- Timely pulse checks to gather real-time feedback
- Aligning employee performance with both organizational and personal goals through frequent measurement and incremental improvement
- Continuous communication to build meaningful relationships and address issues before they impact productivity.
Regular Feedback Loops
Regular feedback loops are an integral part of talent management in Agile HR. These loops involve frequent check-ins that provide timely and relevant feedback, essential for immediate course corrections and performance improvement.
Benefits of regular feedback loops include:
- Reducing the pressure associated with annual reviews
- Maintaining high employee engagement
- Ensuring consistent communication
- Quick resolution of workplace issues.
Effective feedback loops consist of four core components:
- Information gathering – collecting quantitative (ex. absenteeism rate, on-time goal completion) and qualitative data (ex. manager or client feedback) about employee performance
- Analysis – reviewing data and identifying patterns and root causes for positive or negative performance
- Action – deciding how to act on the issue
- Notification – notifying the employee of performance results, analysis, and actions to be taken
While these steps may seem tedious on paper, in real-time, agile practices could be as simple as hearing positive feedback about project response time from both a manager and a client, seeing this pattern, and telling the employee that they did a great job.
Employee Empowerment
Employee empowerment is a significant element of Agile for HR. Continuous feedback in agile performance management empowers employees by making them aware of expectations and performance in real-time. This proactive approach encourages employees to take ownership of their roles and promotes ongoing development.
Empowered employees are more likely to stay with the company as they feel valued and heard through regular feedback. By directly connecting their actions to company objectives, an agile HR mindset fosters a sense of ownership and pride in employees’ work.
Enhancing Talent Management with an Agile HR Approach
By implementing agile recruitment strategies and continuous learning and development initiatives, Agile improves the talent management process for HR. Agile cultivates a culture of continuous learning and innovation, creating valuable experiences for employees that go beyond their expectations. This approach not only maximizes the potential of existing talent but also reduces recruitment and training costs.
Agile Recruitment Strategies
Agile recruitment strategies are crafted to quickly adapt to evolving talent requirements, and leverage agile practices like sprints and iterations to make talent management and hiring a more efficient and constantly-improving process.
In fact, the talent acquisition team at Thales, a European technology and security company, was able to improve performance by 72% over 9 months using an Agile human resources method.
Hiring sprints put the agile model into practice by quickly achieving recruitment goals. Sprints may be broken into sections of the hiring process, typically for 2-3 weeks, like:
- Planning: Identifying roles to be filled, planning job positions, getting approvals
- Promoting: Promoting the open positions (internally and on career websites, social media, etc.)
- Evaluating: Reviewing resumes, interviewing candidates, etc.
- Decision: Analyzing all data gathered during evaluation process and deciding who to hire, notifying candidates
Utilizing advanced analytics and artificial intelligence can further assist in identifying skill gaps during the planning phase, and ensure that recruitment efforts are targeted and effective.
Additionally, job roles should be flexible in nature so talent can adapt to market fluctuations, ensuring that the organization remains competitive.
Continuous Learning and Development
Agile HR considers continuous learning and development as crucial components. By fostering a culture of continuous learning, Agile HR encourages the exchange of ideas and knowledge. Comprehensive learning programs and workshops, along with job rotation and skill-sharing programs, support ongoing development and innovation.
Agile can be integrated with learning and development to facilitate rapid learning by breaking learning goals into sprints.
Agile HR also provides mentorship opportunities to support skill development, ensuring that employees are always growing and improving. Learning and development KPIs can help evaluate the efficiency of learning initiatives and inform decision-making.
Building a Culture of Psychological Safety
Fostering a culture of psychological safety in Agile HR requires the encouragement of open communication and the support of risk-taking and innovation. Psychological safety at work allows individuals to express their thoughts and ideas without fear of negative consequences, fostering trust and inclusivity.
Creating a psychologically safe environment encourages employees to take risks and provide honest feedback, which is critical for innovation and growth. This cultural shift requires a change in mindset and everyday behaviors but is essential for fostering a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability.
Encouraging Open Communication
Agile HR deems open communication as crucial since it nurtures trust, inclusivity, and collaboration among team members. Frequent feedback sessions and one-on-one check-ins promote a culture of transparency and mutual trust in the workplace. Providing a platform for anonymous suggestions can help employees feel comfortable sharing ideas and concerns that they might not address otherwise.
Acting on feedback by acknowledging and considering suggestions is crucial for maintaining open communication and ensuring that employees feel heard and valued.
Supporting Risk-Taking and Innovation
In Agile HR, backing risk-taking and innovation cultivates a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability. Leaders play a key role in promoting risk-taking by acknowledging and rewarding innovative ideas, even if they don’t always succeed.
There is a high correlation between a strong coaching culture and improved organizational performance and employee engagement. By fostering an environment where employees are not afraid of failure and are encouraged to experiment, Agile HR creates a culture of innovation and growth.
Measuring Success: Agile HR Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
The success of Agile HR initiatives is determined by monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and making decisions based on data. Exit Interview Participation and Feedback gather insights from departing employees about their reasons for leaving, providing valuable data to enhance retention strategies.
To gauge the effectiveness of Agile HR implementations, it is essential to measure various metrics and KPIs. These indicators provide insights into how well Agile HR practices are achieving their goals and where improvements may be needed.
For assessing the success of performance management, employee engagement, and talent management initiatives, KPIs in Agile HR are indispensable.
KPIs can be applied in nearly every facet of human resources:
- Performance management metrics: Goal achievement rate, performance appraisal completion rate, 360-degree feedback participation rate
- Employee satisfaction and loyalty: Employee Net Promoter Score (eNPS), Employee Satisfaction Index, absenteeism Rate, employee survey participation levels.
- Talent acquisition and recruitment: Time to fill, cost per hire, source of hire, offer acceptance rate, quality of hire
- Retention and turnover: Employee turnover rate, voluntary vs. involuntary turnover, retention rate of high performers
- Employee Value Proposition: Employee satisfaction scores, cost per hire, turnover rates, online review
- Learning and development: Training completion rate, Return on Investment (ROI) for learning and development
These metrics help in optimizing the impact of agile teams in HR, as well as the overall business objectives. They also inform data-driven decision making, a hallmark of agile business practices.
Summary
In summary, mastering Agile HR involves understanding its principles, implementing key practices, and continuously measuring success. By fostering collaboration over hierarchy, responding swiftly to change, and promoting continuous improvement, Agile transforms the traditional HR function into a dynamic and responsive powerhouse.
The benefits of adopting Agile HR are clear: enhanced organizational agility, increased employee satisfaction, and improved overall performance. Embrace the agile approach and watch your HR function—and your organization—thrive in today’s fast-paced business environment.


